With the creation of the genesis Bitcoin block in 2008, Satoshi’s philosophy was clear: to create a decentralized currency free of control by the very institutions who had been controlling the monetary system, and thus the people, for far too long. People are hungry – better yet, starving – for an alternative to the central institutions that have failed them far too long.
Now, with the rapid rise of DeFi over the past year, it is evident people want more than just a decentralized currency. They want a decentralized system.
Decentralized finance, or DeFi for short, is the new hottest thing in the crypto and blockchain space. In essence, DeFi takes existing financial products and services – loans, borrowing, trading, and more – and puts them on the blockchain. By placing these financial products and services on the blockchain, the middle man is taken out of the equation.
Source: Twitter.com
It is necessary to mention that these financial services on the blockchain are not entirely decentralized. This is because many of the DeFi products currently offered still have a centralized company behind the smart contract that their product operates on. However, these centralized companies still have far less control and impact over your finances than the typical central authorities – banks and governments
Many suggest “non-custodial finance” as the more accurate term (albeit, far less catchy). What non-custodial means is that you still hold the keys to your crypto and don’t have to hand them over to a trusted intermediary. Instead, you retain complete control over your crypto while your transactions are being carried out via smart contracts.
How DeFi Works – Smart Contracts and DApps
DeFi services exist primarily on the Etherium (ETH) blockchain, where financial services are carried out by smart contracts.
What is it that smart contracts do well?
- Remove middlemen from the equation: Middlemen are often costly and can cause time delays in a financial transaction. Smart contracts make it possible for parties to exchange anything of value without needing to go through an intermediary like a bank.
- Solve the ‘who sends first’ issue: There’s a question of trust in financial exchanges between parties. Someone needs to take the first step, but that involves putting themselves at risk. Smart contracts fix this by only executing once all parties have done their part.
- Enable custom rule criteria: The beauty of smart contracts is they make transactions more programmable. Users are able to set transactions so they can’t be completed until all the preset rules are fulfilled.
- Make the transactions more transparent: Due to the increased level of transparency, it’s easier to trust other parties in transactions. This is because every single transaction carried out by smart contracts is recorded on the public blockchain.
To illustrate, say Jim wants to send his son Mike 1 ETH on the first of every month, which he can easily set as a custom rule criterion of the contract. So, on the first of every month, Mike will receive 1 ETH without Jim even having to click a button. By using a smart contract, Jim does not have to pay the fee that a bank (the middleman) would charge for sending a cheque or e-transfer. As well, he does not have to worry about sending each ETH on the first of the month, as this was written into the smart contract code.
This example illustrates smart contracts in their most basic form. However, smart contracts serve a much more important purpose in the DeFi space than simply sending and receiving cryptocurrencies. Smart contracts are used by developers to create DApps (Decentralized Applications), which are the applications that DeFi products and services run on. Since these apps are built using smart contracts, they are inherently decentralized.
In With the New and Out with the Old
DeFi has grown massively over the past year. The main metric to measure DeFi adoption is ‘Total Value (USD) locked in DeFi’. In January 2019, this value was around $320 million. Fast forward to January 2020 – $815 million. And now, 6 months later – $1.57 billion.
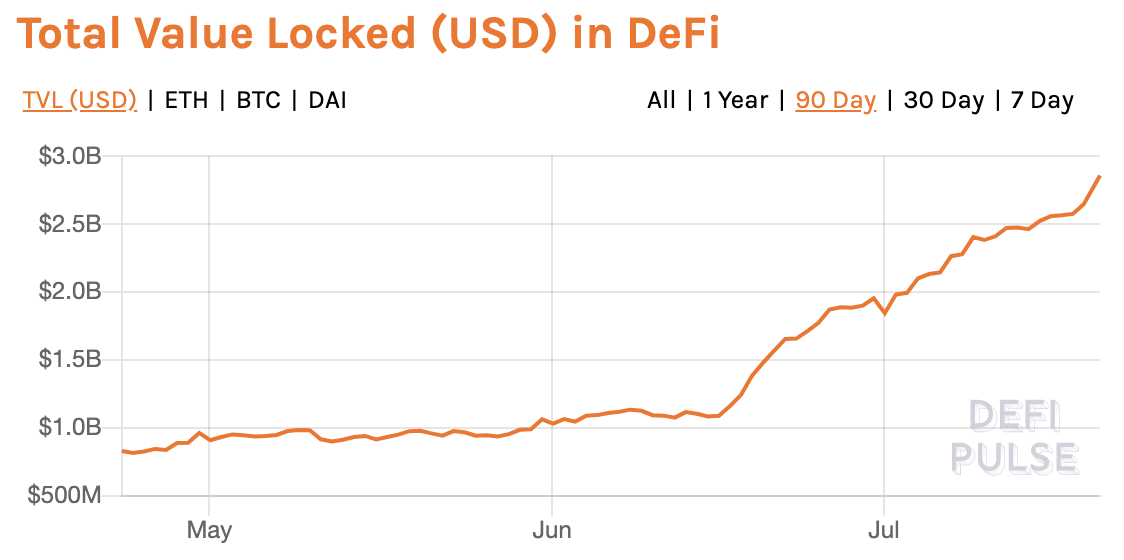
Source: Defi Pulse
Its growth and adoption are undeniable. Why? To answer this question, we have to ask: what is wrong with the traditional financial system?
The global financial system is (mainly) comprised of central banks, massive financial institutions, and government regulations. This system has become increasingly centralized, meaning fewer authorities have control over it, which results in money and power being distributed among fewer people. Yes, this centralization has created more wealth, but it has also led to several problems.
Here are some major flaws of the current centralized system:
- Major income inequality. Billions – 1.7 Billion to be exact – remain unbanked (according to the World Bank). The main reason being many do not have enough money for it to be worth them creating one. Also, many cite ‘distrust’ of institutions, especially in developing countries.

Source: World Bank
- High intermediary costs and Slow Transactions. In a world becoming more connected by the day, global payments-especially remittances – are increasingly necessary. These should come at low costs, and be done quickly. However, this is not the case. On a global average, people spend 7% of the money they send on transaction fees.
- Low Trust in Financial Institutions and Governments. Globally, the financial sector is the least trusted sector (with education and technology ranking as the most trusted).
DeFi has the answers to all of these problems. It will democratize finance by opening it up to a global audience of participation.
How it can do so is better understood by looking at current use cases and DApps available.
DeFi Apps and Uses
Right now, the most popular DeFi product is MakerDAO, a stablecoin and decentralized reserve bank project. Each of its stablecoins (DAI) are pegged to the USD, which allows it to have the stability of fiat currency while having the decentralized, non-custodial, and permissionless qualities of a cryptocurrency.
For citizens of developing nations – such as Venezuela and Zimbabwe – experiencing high inflation and currency volatility, investing in DAI provides a stable store of value that retains worth regardless of their government's monetary policy. Other stablecoins have emerged, such as USD Coin (USDC) and Tether (USDT), which are both pegged to the USD.
The most common uses of DApps in the DeFi space are borrowing and lending, which is primarily done on Compound. First, it is important to understand how taking out a loan in the crypto space works.
Assume I walk into a bank, and want to borrow $10,000. The bank would look at my current balance and credit score to determine whether I am a customer who will likely pay back his loan.
This is not how it works in the DeFi space, where there are no KYC or credit checks; this is part of what makes the space beautiful and encourages members from all over the globe – regardless of where they come from or their financial history – to participate. However, as these security measures do not exist, to take out a loan, one must put down collateral in the form of cryptocurrency (ETH for example) which will be locked up in what is called a collateralized debt position (CDP) which will be overcollateralized. What this means is that you must put down more money than what you are taking out, so be careful!
Compound is also a great place for lending. Using DAI as an example, people can lend out their DAI and earn interest on their tokens. However, the interest rates are often much higher than one would receive in a savings account, ranging between about 6-10%. LoanScan.io is a site where users can compare interest rates on different DeFi platforms, in order to make the most of their lending.
This has major implications for those in the developing world. As previously mentioned, investing in a stablecoin like DAI can be beneficial for those looking to hold a store of value in an inflationary economy. Lending in the DeFi space takes this one step further by allowing those citizens of developing nations to not only hold a store of value, but make money in interest off of it.
DeFi trading platforms are becoming increasingly adopted. Dydx exchange is the first DApp to offer non-custodial margin trading of ETH or DAI. It enables users to short or long the aforementioned currencies in a decentralized way, meaning you retain control over your assets the entire time; no need to trust a broker to handle them for you.
Token Sets is another emerging DApp gaining popularity. You can think of it as an automated crypto portfolio manager. Say I want 60% of my portfolio balance to be in ETH and the other 40% in BTC. With the constantly changing market values, it would be a pain for me as the consumer to constantly monitor and rebalance my portfolio. This is where Token Sets comes into play. At the end of each month, it will automatically rebalance my account for me.
Looking Forward
“Crypto isn’t the money of the internet. It is the internet of money” - Andreas Antonoplous, Bitcoin advocate and entrepreneur.
We use the internet for everything. Very soon, according to Andreas, we will use crypto for everything. As we all know, crypto has been met by a countless number of skeptics and disbelievers, such as the wealthy and well-known Warren Buffett.
However, there was a time when very smart and wealthy people were skeptical about the practicality and longevity of the internet. Robert Metcalfe, the inventor of Ethernet, said “I predict the internet will in 1996 catastrophically collapse”. How did that prediction pan out?
To predict whether or not something will be a “thing” of the future, one must look at a) its foundational philosophy and b) its potential uses.
Every single financial tool, service, or product may one day exist on the blockchain, in the cryptosphere. We already see issuance, exchange, lending, borrowing, derivatives, insurance, and many more.
What’s next?
First, the DeFi space would gladly welcome a form of under-collateralized loans, comparable to that of taking out a mortgage on a house. In essence, you (the borrower) still have to put up collateral, however, you have to put up less than the value of the assets you are receiving. This would require a blockchain-based loan reputation system. Tricky, but certainly doable.
Second, insurance is a promising use-case in the DeFi space to combat the issue of bugged smart contracts being hacked, which has infamously happened in cases such as the DAOs IPO, where $60 million in assets were stolen. DApp developers such as Nexus Mutual are leading the charge in this space.
Next, the role developing countries play in expanding DeFi is both exciting and promising. Many South American and African countries are experiencing severe inflation, resulting in a devalued local currency. As mentioned, assets such as DAI or UDSC provide an opportunity to citizens of these countries to preserve their purchasing power and earn interest while doing so. One aspect which surely needs to be improved upon in this pursuit of financial democracy is the understandability of DeFi; undoubtedly, it can be a complicated concept to wrap one's head around.
Finally, a shift from what is “non-custodial” finance to truly decentralized finance is the last frontier. We are likely a ways away from this, but with continued growth, this goal is within reach.
Conclusion
The rapidly growing DeFi space is full of potential. The current vision contains so many possibilities, and could cause major disruption to the current financial system led by banks, financial institutions, and government regulations. If this vision is realized, these middlemen will be cut out, thereby reducing global monetary inequalities, reducing global transaction costs, and altogether cutting reliance on these already mistrusted institutions.
The current dApps offered have strong use cases in the lending, borrowing and trading spaces. We all hope to see the space live up to its massive potential, and become the leading and trusted mode of finance worldwide.






